Partners
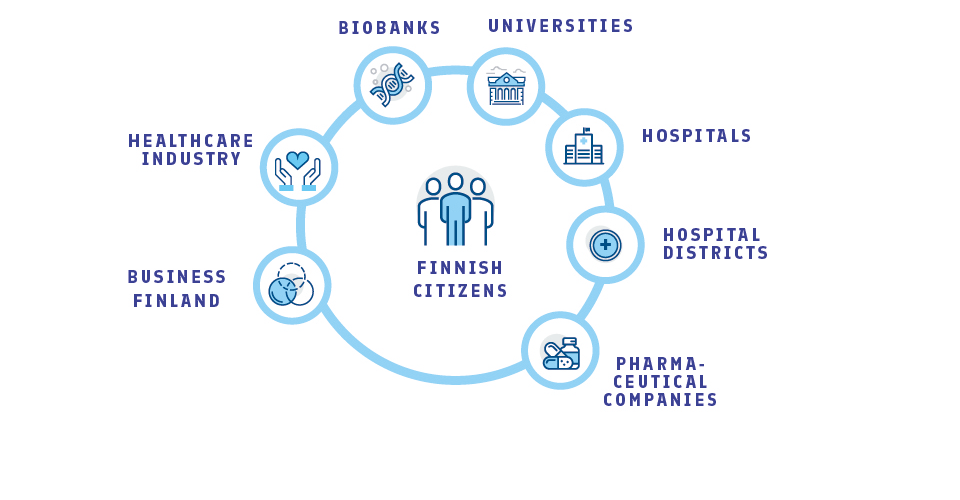
The FinnGen research project involves all the same actors as drug development: universities, hospitals, biobanks and pharmaceutical companies. With this open cooperation, we hope to speed up the emergence of new innovations.
Coordinating organizations:
University of Helsinki (Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland, FIMM) is coordinating the FinnGen study. Helsinki Biobank (the Hospital District of Helsinki and Uusimaa) coordinates the sample collection and THL coordinates the processing of register data.

Funded by:

and the funding research partners:
AbbVie, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech (a member of the Roche Group), GSK, Janssen, Maze Therapeutics, MSD/Merck, Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi.

In cooperation with the Finnish Biobank cooperative FINBB and these Finnish biobanks:
Biobank | The background organization that has signed the consortium agreement for the biobank | Biobank logo |
|---|---|---|
Auria Biobank | Wellbeing Services County of Southwest Finland University of Turku |  |
Northern Finland Biobank Borealis | Wellbeing Services County of North Ostrobothnia University of Oulu |  |
Arctic Biobank | University of Oulu |  |
Central Finland Biobank | Wellbeing Services County of Central Finland University of Jyväskylä |  |
Finnish Clinical Biobank Tampere | Wellbeing Services County of Pirkanmaa Tampere University Foundation sr |  |
Biobank of Eastern Finland | Wellbeing Services County of North Savo University of Eastern Finland |  |
Helsinki Biobank | HUS, University of Helsinki |  |
THL Biobank | The Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare |  |
FRC Blood Service Biobank | The Finnish Red Cross Blood Service |  |
FHRB Biobank | Finnish Association of Haematology |  |
Finnish Biobank Cooperative (FINBB) |  |